
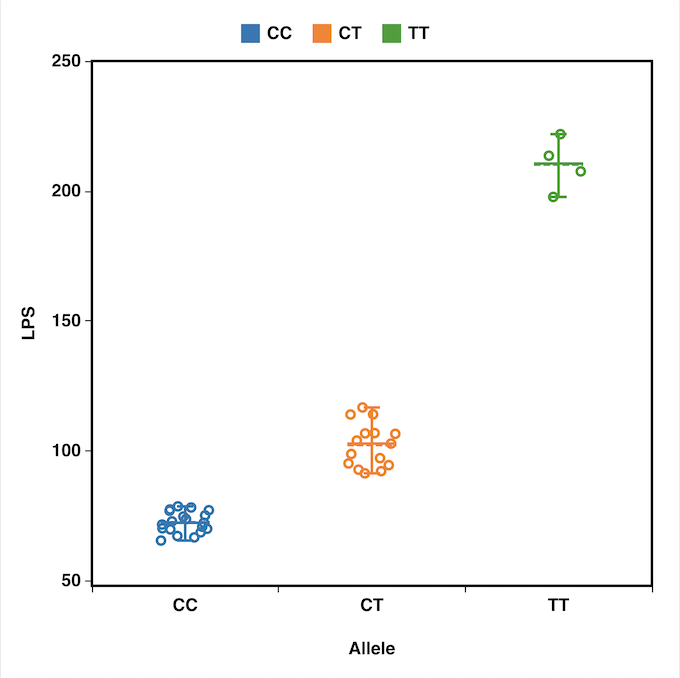
The IQR for the first data set is greater than the IQR for the second set. The first data set has the wider spread for the middle 50% of the data.There are 16 data values between the first quartile, 56, and the largest value, 99: 75%. There are five data values ranging from 82.5 to 99: 25%. There are five data values ranging from 74.5 to 82.5: 25%. There are six data values ranging from 56 to 74.5: 30%. Day class: There are six data values ranging from 32 to 56: 30%.Which box plot has the widest spread for the middle 50% of the data (the data between the first and third quartiles)? What does this mean for that set of data in comparison to the other set of data?.Create a box plot for each set of data.For each data set, what percentage of the data is between the smallest value and the first quartile? the first quartile and the median? the median and the third quartile? the third quartile and the largest value? What percentage of the data is between the first quartile and the largest value?.Find the smallest and largest values, the median, and the first and third quartile for the night class.Find the smallest and largest values, the median, and the first and third quartile for the day class.The top 25% of the values fall between five and seven, inclusive. At least 25% of the values are equal to five. Twenty-five percent of the values are between one and five, inclusive. In this case, at least 25% of the values are equal to one. For example, if the smallest value and the first quartile were both one, the median and the third quartile were both five, and the largest value was seven, the box plot would look like: The right side of the box would display both the third quartile and the median. In this case, the diagram would not have a dotted line inside the box displaying the median. For instance, you might have a data set in which the median and the third quartile are the same. This video explains what descriptive statistics are needed to create a box and whisker plot.įor some sets of data, some of the largest value, smallest value, first quartile, median, and third quartile may be the same. The middle 50% (middle half) of the data has a range of 5.5 inches.The interval 59–65 has more than 25% of the data so it has more data in it than the interval 66 through 70 which has 25% of the data.Range = maximum value – the minimum value = 77 – 59 = 18.So, the second quarter has the smallest spread and the fourth quarter has the largest spread. The spreads of the four quarters are 64.5 – 59 = 5.5 (first quarter), 66 – 64.5 = 1.5 (second quarter), 70 – 66 = 4 (third quarter), and 77 – 70 = 7 (fourth quarter).Each quarter has approximately 25% of the data.The following data are the heights of 40 students in a statistics class.ĥ9 60 61 62 62 63 63 64 64 64 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 65 66 66 67 67 68 68 69 70 70 70 70 70 71 71 72 72 73 74 74 75 77Ĭonstruct a box plot with the following properties the calculator instructions for the minimum and maximum values as well as the quartiles follow the example. The box plot gives a good, quick picture of the data. The median or second quartile can be between the first and third quartiles, or it can be one, or the other, or both. The “whiskers” extend from the ends of the box to the smallest and largest data values.

Approximately the middle 50 percent of the data fall inside the box. The first quartile marks one end of the box and the third quartile marks the other end of the box. The smallest and largest data values label the endpoints of the axis. To construct a box plot, use a horizontal or vertical number line and a rectangular box.
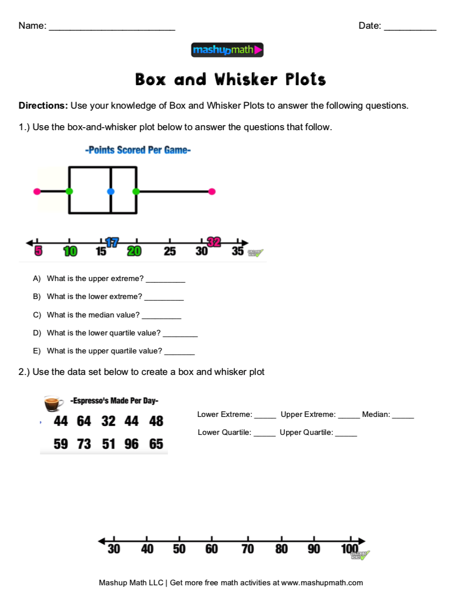
We use these values to compare how close other data values are to them. A box plot is constructed from five values: the minimum value, the first quartile, the median, the third quartile, and the maximum value. They also show how far the extreme values are from most of the data. Recognize, describe, and calculate the measures of location of data: quartiles and percentiles.īox plots (also called box-and-whisker plots or box-whisker plots) give a good graphical image of the concentration of the data.Display data graphically and interpret graphs: stemplots, histograms, and box plots.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
